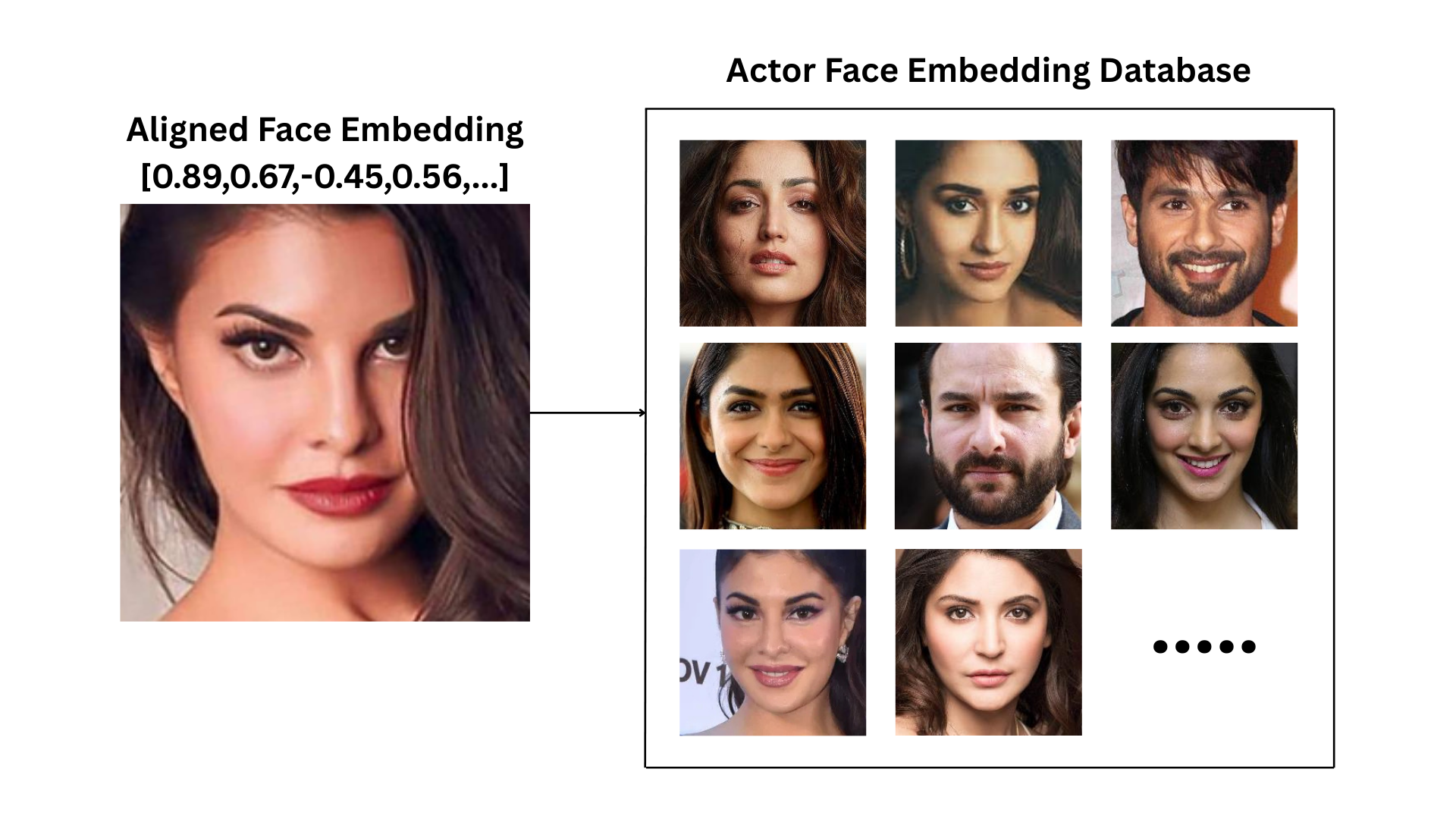
Face Embedding
Siamese Network
- A Siamese Network is a type of neural network architecture that consists of two or more identical subnetworks, which share the same parameters, weights, and architecture. The purpose of this architecture is to learn a similarity function rather than a classification function.
- Siamese networks take in two input samples and pass them through the twin networks, producing embeddings (feature representations). These embeddings are then compared using a distance metric (such as Euclidean distance or cosine similarity) to determine whether the two inputs are similar or dissimilar.
- The model is trained with triplet loss, encouraging similar inputs to have closer embeddings and dissimilar inputs to have farther embeddings.
Triplet Loss
Triplet Loss is a loss function used to train models like Siamese Networks to learn similarity-based representations more effectively. The goal is to ensure that the anchor-positive distance is smaller than the anchor-negative distance by a margin. It operates on triplets of samples:
- Anchor (A): The reference sample.
- Positive (P): A sample similar to the anchor.
- Negative (N): A sample different from the anchor.