Face Recognition
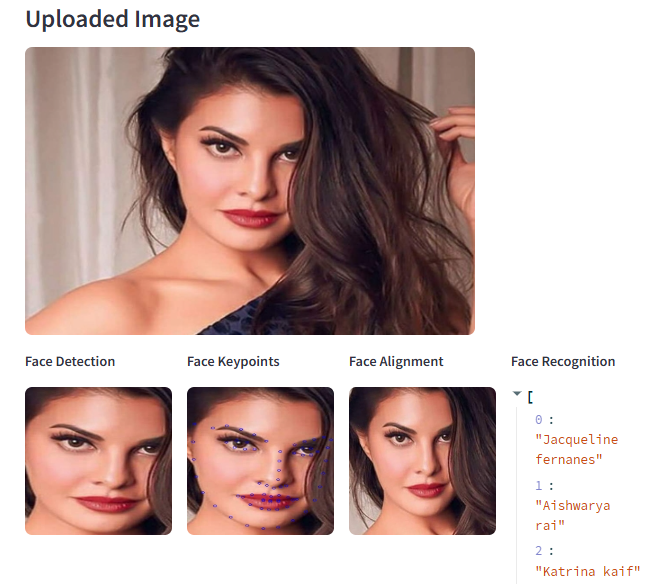
A face recognition system follows a structured pipeline:
Face Detection → Landmark Detection → Face Alignment → Face Embedding Generation → Face Recognition
1. Face Detection
- The first step in face recognition is detecting the face in an image or video.
- It involves identifying the location of faces and drawing bounding boxes around them.
- Faster RCNN Model is used for face detection.
2. Face Keypoint Detection
- Once a face is detected, key landmarks on the face (e.g., eyes, nose, mouth, jawline) are identified.
- These keypoints help in further processing such as alignment and feature extraction.
- Dlib’s facial landmark detector, and MediaPipe are used for this task.
3. Face Alignment
- Faces in images may have variations due to different angles, lighting conditions, and expressions.
- Face alignment ensures all faces are oriented in a consistent manner before feature extraction.
- This step uses the detected keypoints for aligning eyes along a horizontal axis.
4. Face Embedding Generation
- After aligning the face, a deep learning model extracts a feature vector (embedding) that uniquely represents the face.
- The Siamese network is used to convert a face into a high-dimensional feature vector.
5. Face Recognition
- The generated embeddings are compared with stored embeddings in a database using similarity metrics like Euclidean Distance.
- Based on the similarity score, the system verifies whether two images belong to the same person.